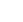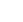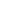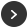What is a Thermal Robot Protection Cover?
Automation has become a critical driver of productivity across almost all industrial sectors. Its impact is especially evident in manufacturing and construction environments, where complex yet repetitive assembly processes are increasingly handled by industrial robotic systems. The development of industrial robots can be traced back to the 1960s, driven by advances in semiconductor technology and the emergence of integrated circuits, which accelerated the evolution of computer-controlled automation.
The deployment of robots in construction and manufacturing delivers measurable operational benefits. Robotic systems reduce reliance on manual labor, shorten production cycles, improve output consistency, and enhance workplace safety by limiting human exposure to hazardous or extreme operating conditions. However, these systems require substantial capital investment, and their long-term value depends heavily on effective protection and maintenance throughout their service life.
Robot protective covers are engineered to address this requirement by shielding robotic equipment from harsh environments, contamination, and mechanical wear. This article provides a practical overview of robot protection covers, focusing on material selection, structural design considerations, and key performance characteristics in industrial applications.
Why Use a Robot Protection Cover?
Industrial robots are commonly deployed in harsh operating environments, including aluminum smelters, foundries, petrochemical plants, steel mills, and refineries. These settings expose equipment to multiple risk factors such as extreme temperatures, chemical vapors, molten splash, dust, humidity, and mechanical abrasion. While these hazards are well known for their impact on worker safety, they can also cause accelerated wear, corrosion, or sudden failure of high-value robotic systems.
Thermal robot protection covers function as a critical barrier between the robot and its environment. They are designed to protect sensitive components from thermal stress, chemical attack, contamination, and mechanical damage, thereby extending service life and preserving consistent operational performance. Proper protection allows robotic systems to operate reliably across a wider range of industrial conditions and reduces unplanned downtime.
Material selection and design must be aligned with the specific application. A cover that provides effective waterproofing to prevent moisture-related electrical failures may not offer sufficient resistance to abrasion, chemicals, or radiant heat. For this reason, each robot protection cover should be engineered according to the actual exposure risks of the operating environment to ensure balanced and long-term protection.
Key Environmental Risks Addressed by Robot Protective Covers
Industrial robotic systems are frequently exposed to environmental conditions that can degrade performance, shorten service life, or cause unexpected downtime. Robot protective covers are engineered to mitigate the following key environmental risks:
1. Extreme Temperatures
High radiant heat, molten splash, and thermal cycling are common in foundries, metal processing lines, and heat-treatment areas. Properly selected protective covers provide thermal insulation and flame resistance to protect joints, cables, and sensitive components from heat-related damage.
2. Chemical Exposure
Chemical vapors, acids, alkalis, oils, and solvents present in petrochemical, surface treatment, and processing environments can accelerate corrosion and material degradation. Chemically resistant cover materials help prevent direct contact and prolong equipment lifespan.
3. Moisture and Humidity
Water ingress from washdown processes, condensation, or high-humidity environments can lead to electrical faults and corrosion. Waterproof and sealed cover designs reduce the risk of moisture penetration while maintaining necessary flexibility.
4. Dust and Particulate Contamination
Fine dust, metal particles, and abrasive debris can accumulate on robotic components, interfering with motion accuracy and increasing wear. Protective covers act as a barrier, limiting contamination and reducing maintenance frequency.
5. Mechanical Abrasion and Impact
Repeated contact with sharp edges, rough surfaces, or debris can cause premature damage to exposed hoses and joints. Abrasion-resistant outer layers enhance durability in high-contact operating zones.
6. Electrical and Static Risks
In certain applications, electrostatic discharge (ESD) or electrical exposure presents additional risks. Insulating or ESD-safe materials can be incorporated to improve operational safety and system reliability.
Tehu Robot Protection Covers
Tehu designs and manufactures high-performance robot protection covers engineered for demanding industrial environments. Our covers are developed to withstand a wide range of mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical exposure risks. Each system is designed to fully enclose robotic arms with a durable yet flexible protective structure, offering flame resistance, corrosion protection, and electrical insulation without restricting robot movement or precision.
All robot protection covers are manufactured on a made-to-order basis. This approach ensures accurate fitting to specific robot models, motion paths, and operating conditions, resulting in reliable protection and long-term operational stability.
For technical specifications or application-specific requirements, our engineering team is available to provide direct consultation. Please contact us to discuss your project in detail.